jewish burial customs embalming
Both Islam and Judaism highly regulate the burial of the deceased within their communities. In contrast reform Jews accept cremation and it is becoming a very popular practice.

Chevra Kadisha Ensures Jewish Burials Follow Rituals Traditions Community Review
Prayers including the Mourners Kaddish are.

. Customarily they make the casket out of wood including. The burial is an important part of Jewish funeral customs. Shiva means seven and is a seven-day mourning period that is observed.
A fundamental principle of Jewish belief the impurity of the dead underpins many of the customs related to death and burial defined in halakhic law for example Numbers 19. Displaying of the body prior to burial does not take place. After the death the deceaseds body is washed carefully and wrapped up in a simple shroud.
In the Quran a crow is sent by Allah to show Cain how to bury his. It is called this way because at Jewish. Burial is intended to take place in as short an interval of time after death as possible.
Just as there is a way to live as a Jew there is also a way to die and be buried as a Jew writes Blu Greenberg in her book How to Run a Traditional Jewish Household Fireside 1983. Therefore embalming is forbidden. A wake ie visiting the funeral home on the night before the burial to comfort the mourners and to view the remains is not a Jewish custom.
Saying Goodbye to a Loved One. When it comes to cremation Jewish funeral customs will vary across Judaism movements. A Jewish funeral ceremony is called a ceremony is called a Levayah accompaniment.
By Lisa Alcalay Klug. Embalming and Viewing the Remains. Because Jewish burial laws require that the body be allowed to become a part of the.
The one thing expressed most clearly by Israelite burial practices is the common human desire to maintain some contact with the community even after death through burial in ones native land at least and if possible with ones ancestors. John 1939 40. Embalming practised in Egypt Gen.
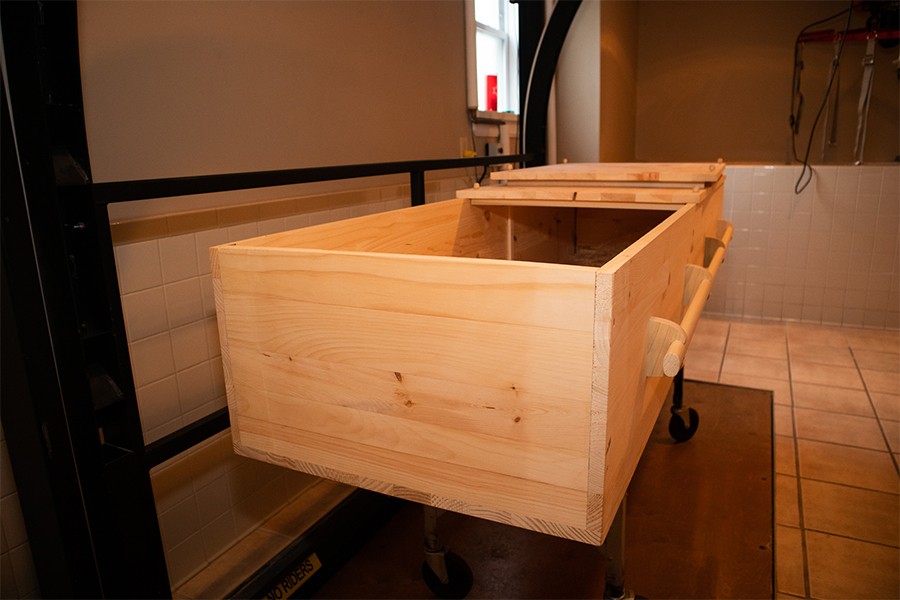
Watchers Chevra Kadisha remain. Jewish law prohibits Cremation and embalming. Traditional Jewish funerals use only natural materials for the casket.
Bible accounts of funerary arrangements reveal that the Jews took great care in preparing the corpse for interment. Perhaps one of the stronger horrors that a Jewish person could imagine was stated in Psalm 78. The immediate family begins sitting shiva.
Embalming is the artificial treatment of a corpse to. The ancient Egyptians may have simply tried to dry corpses in the hot desert sands or as in one of the chambers found at Thebes in rooms which were artificially heated. Traditional Jewish funeral customs will not display the deceased body.
Bury me with my fathers Jacobs request Gen. 2 26 and in the case of Aristobulus in Rome Josephus Ant xiv. After a Jewish funeral takes place the immediate family ie spouse parents children and siblings are considered the mourners.
Surely the emphasis on the body in the funeral service serves to weaken the spiritual primacy and traditional religious emphasis on the soul. Here are a few common Jewish burial customs and Jewish death rituals. A small group of people known as the Chevra Kadisha remain with the body until the funeral is conducted.
It is traditional Jewish practice to perform a ritual washing of the body Tahara and then to dress it in a plain burial shroud. They will conduct the Taharah cleansing of the body dress the deceased in the tachrichim and otherwise ensure that the burial is conducted in accordance with Jewish tradition. The dead must be separated by a distance from places of human habitation and confined to areas for them alone.
Its important to note that cremation is generally not a part of the Jewish tradition and that embalming is also avoided. The family remains at home in a shiva house. Both embalming and cremation are traditionally forbidden though many Jewish communities have started to accept cremation.
The preparation and interment of the body should be entrusted to the local Chevra Kadishah. For example Orthodox and Conservative Jews prohibit it as they believe the body should be buried in the ground intact. Acts 936-41 Neighbors and others could come to express their grief and console the family.
The Hebrews buried their dead immediately no later than a day after the person passed away. The Jewish people took the burial of the dead quite seriously. Jewish funerals emphasize simplicity to avoid embarrassment for the poor.
Burial is considered the best way to allow the body to decompose naturally. When a lengthy delay in. Bender Beliefs Rites and Customs of the Jews Connected with Death Burial and Mourning in Jewish Quarterly Review 1894 and 1895.
There are also strong Jewish beliefs around cremation namely that cremation isnt allowed. Wooden dowels replace the hinges nails or screws used in more modern burials because Jewish custom mandates that the entire casket must be biodegradable. It was the way a community paid its last respects to the one who died.
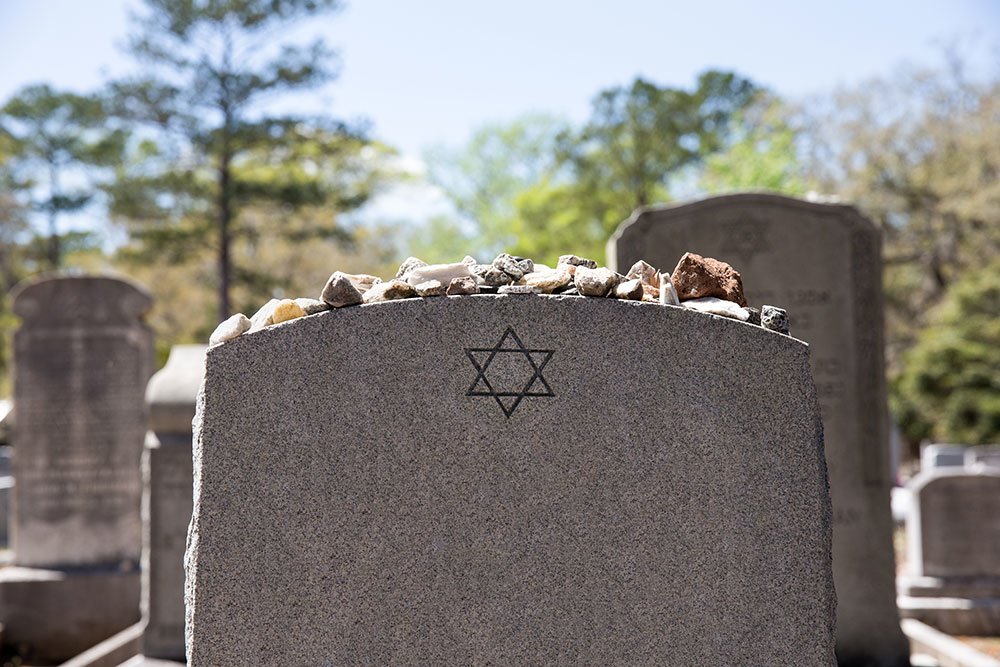
A Jew should be buried only among fellow Jews in a Jewish. Spices and Plants at the Burial. The natural drying out of the body by solar heat mummification is the oldest method of preserving a corpse.
1 Time of Burial. Additionally organ donation is accepted across all. Family and friends washed the body of the deceased rubbed it with spices and fine oil and wrapped it in cloths.
7 4 was unknown or at least exceedingly rare in Judea. According to the Jewish Encyclopedia this custom stems from the Mosaic Law which ordered that any person hung from a tree or cross as a form of execution should be taken down and buried within a day after death. If glue is used to make the casket vegetable-derived glue is used instead of one that is animal-derived.
It will take place either in a Jewish funeral home synagogue or temple and then follow to the cemetary. This classic guide to Jewish living outlines traditional death rituals and. The Scriptures laid down quite firmly that no dead body was to be left unburiedeven that of ones worst enemy.
Thus the importance of cemeteries. As such no embalming is allowed and the funeral is typically closed casket. There are however several exceptions to the general prohibition of embalming.
4929 was the wish of every ancient Israelite. The Jewish tradition tells of a raven that showed Adam and Eve what to do with the body of their dead son Abel by scratching at the earth to reveal the buried body of one of its own. The Jewish funeral consists of a burial also known as an interment.
Customs for reciting the Mourners Kaddish vary markedly among various communities. Once the casket is closed it is not to be opened again unless the deceased was not previously identified and now requires identification.

Jewish Funeral Customs Funeral Partners

Why Don T Jews Have Open Casket Funerals Death Mourning

The Mitzvah Of Burial And The Honor Of The Dead Chayei Sarah 5776 Gateways Org
Complete Guide To Jewish Orthodox Burial Rituals And Caskets Trusted Caskets

Jewish Traditions For Death Burial And Mourning Rohatyn Jewish Heritage

The Tomb Of Jesus First Century Jewish Burials Sagu
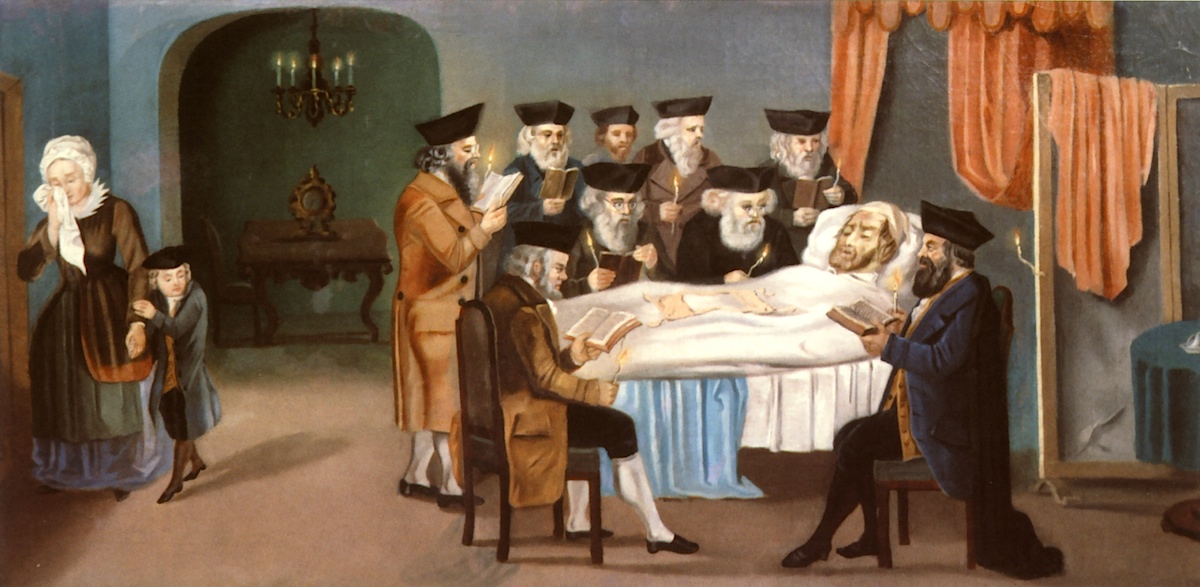
Jewish Traditions For Death Burial And Mourning Rohatyn Jewish Heritage

What Is Jewish Burial South Florida Jewish Cemetery

Jewish Mourning Faq My Jewish Learning
Tahara Supplies For The Chevra Kadisha Jewish Funerals Burial And Mourning
Burial Of Jewish War Veterans In Military Cemeteries Jewish Funerals Burial And Mourning

Jewish Burial Customs Welcome To Willowbrook Cemetery Located In

Closed Caskets At Jewish Funerals Jewishboston

What Is Jewish Burial South Florida Jewish Cemetery

Funeral Customs Black S Funeral Home Thurmont Md Funeral Home And Cremation
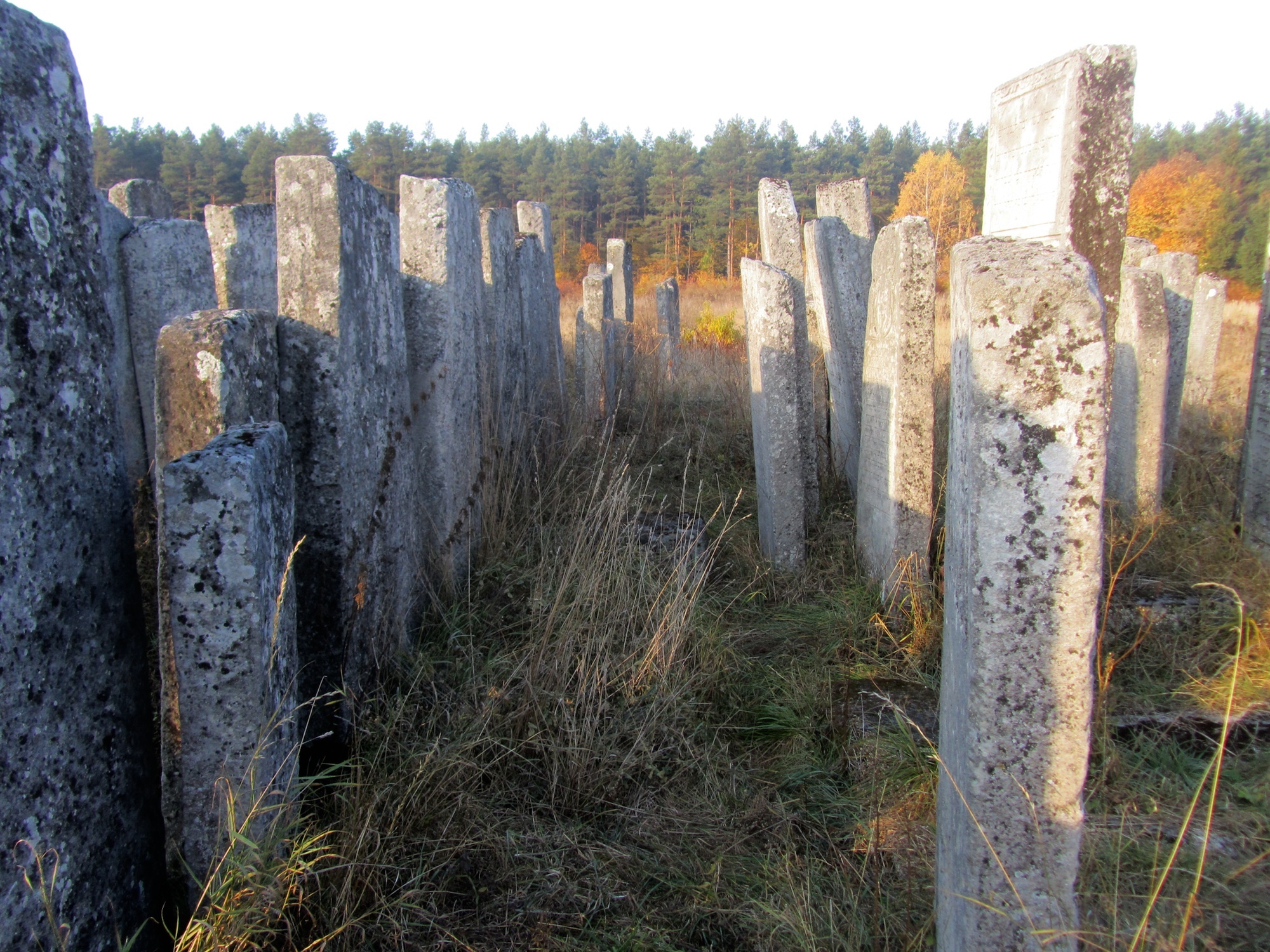

Jewish Traditions For Death Burial And Mourning Rohatyn Jewish Heritage

Jewish Mourning Faq My Jewish Learning
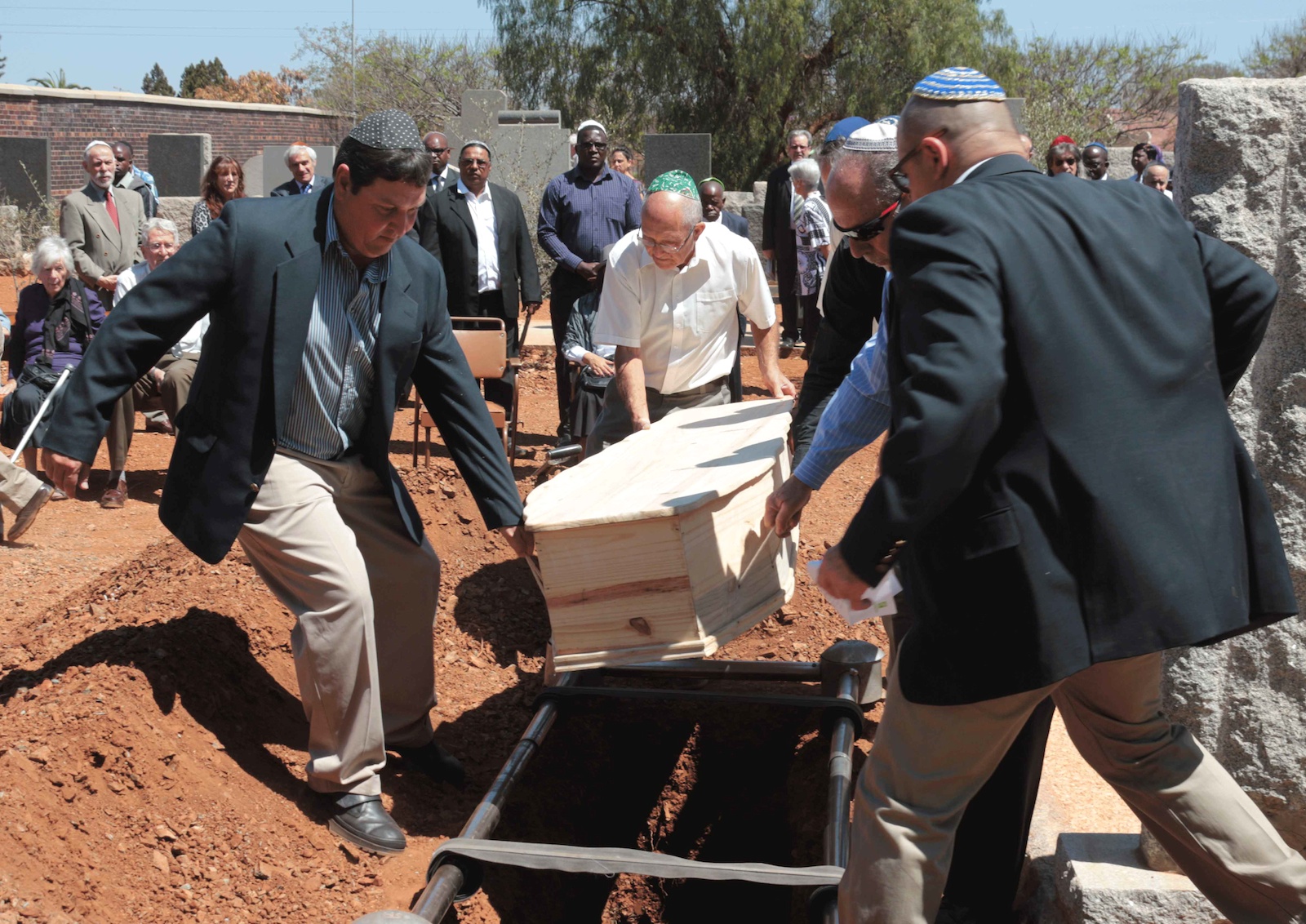

Jewish Traditions For Death Burial And Mourning Rohatyn Jewish Heritage
